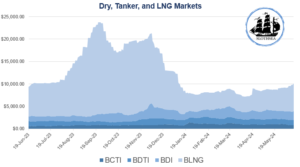
The chart represents the performance of the dry, tanker, and LNG markets in maritime transport between June 2023 and June 2024, through three main indices: the Baltic Tanker Indices (BCTI & BDTI), the Baltic Dry Index (BDI), and the Baltic LNG Index (BLNG).
Baltic Clean Tanker Index (BCTI) & Baltic Dirty Tanker Index (BDTI)
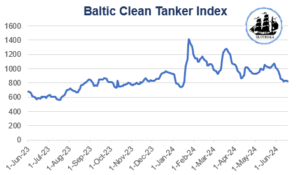
The BCTI and BDTI trend indicates relative stability, with values fluctuating mainly between $600 and $1,400 for the Clean market and between $700 and almost $1,600 for the Dirty market during the period considered. Despite some seasonal fluctuations, the indices did not experience significant changes, indicating stability in the tanker market. This stability can be attributed to a constant demand for refined products and not and a well-balanced transport capacity relative to demand.
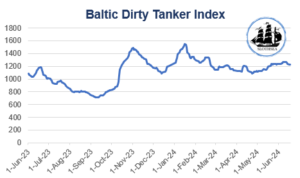
However, geopolitical conflicts, particularly attacks by Houthis in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden, have led to the rerouting of ships away from these areas towards the Cape of Good Hope. This rerouting is expected to impact the market throughout 2024, with normal routing anticipated to resume in 2025. Longer sailing distances are projected to account for 75-80% of the demand growth in 2024, but shorter distances in 2025 could reduce demand. Despite a weak start in the first months of 2024, with tonne miles down 5-6% compared to the previous year, ship prices have remained strong, with new building prices up 33% and five-year-old ship prices up 60%. Secondhand ship prices have approached those of new builds, indicating robust market conditions. Trade restrictions due to sanctions on Russian oil exports and ongoing conflicts are expected to add significantly to crude tanker demand during the whole of 2024.
Baltic Dry Index (BDI)
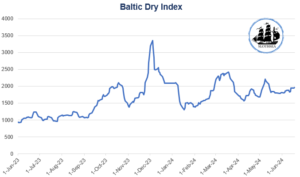
Since September 2023, the Baltic Dry Index has strengthened due to increased demand for capesize vessels. Higher volumes of cargo, including a surge in iron ore shipments from Brazil and the buildup of iron ore inventories in China, have driven up capesize freight rates. In the smaller segments, rerouting away from the Red Sea and the Panama Canal has also boosted demand. Second-hand ship prices have risen significantly, with prices for 5-year-old vessels nearing those of new buildings.
Freight rates are expected to remain robust during the year. As transits through the Red Sea and Panama Canal normalize, sailing distances are expected to shorten. In 2025, freight rates might weaken as supply grows faster than demand.
Capesize vessels are likely to perform best, as their fleet is projected to grow more slowly. Their demand has been driven by higher cargo volumes rather than increased sailing distances due to rerouting. Panamax and supramax ships may face pressure on their earnings due to high ship deliveries and lower demand growth.
There are both upside and downside risks to demand. A prolonged crisis in the Red Sea and continued Panama Canal transit restrictions would likely strengthen the market. Conversely, deteriorating conditions in China’s property or financial sectors could negatively impact demand.
Baltic LNG Index (BLNG)
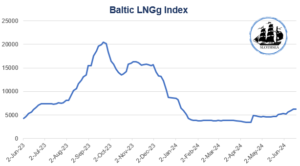
The BLNG registered significant volatility. Starting from June 2023, the index experienced sustained growth, peaking at slightly over $20,000 in October and November 2023. However, this growth phase was followed by a marked decline, bringing the index to stabilize around $5,000 in the subsequent months.
In early 2024, the LNG shipping market underwent significant disruptions. Low water levels in the Panama Canal constrained LNG transits, and by mid-January, movements through the Suez Canal were halted, forcing shipments to take alternative routes. Despite these logistical challenges, LNG demand in Asia remained strong, driven by competitive pricing and strategic stock-building. Northeast Asia saw a 4.02% increase in LNG imports during Q1 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, with China leading this surge. Southeast Asia also experienced substantial growth, particularly in India, Thailand, and Pakistan. In contrast, Europe’s LNG imports fell by 14.84% in Q1 2024, reflecting shifts in energy sourcing and consumption strategies.
In Q2 2024, escalations in the Middle East added another layer of uncertainty. Risks associated with key trade routes, such as the Strait of Hormuz, have become a major concern. If this strait were closed or deemed high-risk, almost a third of the world’s LNG, which transits through this passage, could be affected. This scenario could lead to supply chain disruptions and support higher freight rates due to rerouting and longer voyage times. Such shifts might also challenge Qatar’s market position and strategic growth objectives, with broader implications for global LNG supply contracts and energy security. Hopefully, at the moment this does not appear to occur, but things could get worse in the second half of the year.
Conclusions
The chart highlights the different dynamics of the three main segments of the maritime transport market. While the LNG market experienced notable volatility, the dry bulk and clean tanker markets maintained relative stability. These trends provide important insights for industry operators, suggesting the need for diversified strategies to address the challenges and seize opportunities offered by the different segments of the maritime market.
#Dry #Tanker #LNG #ShippingMarket #Bulkshipping #SlothSea
(Source: Hellenic Shipping & BIMCO & Baltic Exchange)